Intraday Trading involves buying and selling securities within the same trading day, aiming to profit from short-term price fluctuations. While there are numerous strategies one can adopt for intraday trading, I’ll provide you with a list of popular techniques to get you started:
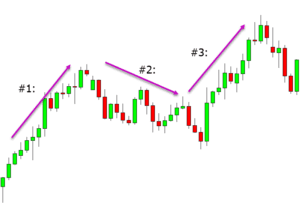
Momentum Trading is a popular strategy used by intraday traders to take advantage of strong price movements in a particular direction. The basic principle behind momentum trading is to identify stocks or other financial instruments that are exhibiting significant price momentum and then enter trades in the direction of that momentum. Here’s an overview of how momentum trading works:
- Identify the Momentum: Look for stocks or assets that are experiencing a notable price move in a particular direction. This could be characterized by a strong upward or downward trend, significant price acceleration, or increased trading volume.
 Confirm the Trend: Verify that the price movement is indeed a sustained trend and not just a short-lived spike or temporary fluctuation. You can use technical indicators such as moving averages, trendlines, or trend-following oscillators like the MACD or the Average Directional Index (ADX) to confirm the trend.
Confirm the Trend: Verify that the price movement is indeed a sustained trend and not just a short-lived spike or temporary fluctuation. You can use technical indicators such as moving averages, trendlines, or trend-following oscillators like the MACD or the Average Directional Index (ADX) to confirm the trend.- Entry Point: Once you have identified a strong momentum trend, plan your entry point. Some traders prefer to enter as soon as the momentum is confirmed, while others may wait for a minor pullback or consolidation before entering to secure a better risk-reward ratio.
- Set Stop-Loss and Take-Profit Levels: Determine your risk tolerance and set appropriate stop-loss and take-profit levels to manage your trade. This helps limit potential losses if the momentum reverses against your position and secure profits if the trend continues in your favor.
- Risk Management: Implement proper risk management techniques, such as position sizing, to ensure that you don’t risk an excessive portion of your trading capital on a single trade. This helps protect your overall portfolio from substantial losses.
- Monitor the Trade: Once in the trade, monitor the price action and the momentum. Adjust your stop-loss and take-profit levels if necessary to protect profits or cut losses.
- Exit Strategy: Determine your exit strategy based on your trading plan. This could be a predefined profit target, trailing stop-loss, or a specific technical or fundamental signal that indicates the trend is reversing.
Breakout Trading is a popular strategy used by intraday traders to capitalize on significant price movements that occur when an asset’s price breaks out of a well-defined intraday trading range or a specific price level. The basic idea behind breakout trading is to enter a trade when the price breaks through a resistance level (in an upward breakout) or a support level (in a downward breakout). Here’s an overview of how breakout trading works:
- Identify the Range: Look for a price range where the asset has been trading within a well-defined boundary. This can be identified using support and resistance levels, trendlines, or chart patterns such as rectangles or triangles.

- Confirm the Breakout: Once you’ve identified the range, closely monitor the price action for a breakout. A breakout occurs when the price convincingly moves beyond the established support or resistance level with increased trading volume, indicating a shift in market sentiment.
- Entry Point: Plan your entry point when the breakout is confirmed. Some traders prefer to enter as soon as the breakout occurs, while others may wait for a retest of the broken level to confirm the strength of the breakout.
- Set Stop-Loss and Take-Profit Levels: Determine your risk tolerance and set appropriate stop-loss and take-profit levels to manage your trade. Place your stop-loss order below the breakout level in an upward breakout or above the breakout level in a downward breakout.
- Risk Management: Implement proper risk management techniques, such as position sizing, to ensure that you have a controlled level of risk on each trade. This helps protect your capital in case the breakout fails and the price reverses.
- Monitor the Trade: Once you’re in the trade, monitor the price action and the strength of the breakout. Adjust your stop-loss and take-profit levels if necessary to protect profits or cut losses.
- Exit Strategy: Determine your exit strategy based on your trading plan. This could be a predefined profit target, trailing stop-loss, or a specific technical or fundamental signal that indicates the breakout is losing momentum or reversing.
Gap Trading is a strategy that involves taking advantage of price gaps that occur on a chart when the opening price of a financial instrument is significantly different from the previous day’s closing price. Price gaps can occur due to overnight news events, economic releases, or other factors that create a disparity in supply and demand. Here’s an overview of how gap intraday trading works:
- Identify the Gap: Look for price gaps on the chart, where the current day’s opening price is significantly higher or lower than the previous day’s closing price. Gaps can be classified as bullish (upward gap) or bearish (downward gap) based on the direction of the gap.

- Classify the Gap Type: Different types of gaps have different implications for trading. Common gap: This type of gap is a temporary break in the price, often filled later in the day or week. Breakaway gap: This gap occurs at the beginning of a strong trend and indicates a significant shift in market sentiment. Runaway gap: Also known as a continuation gap, this occurs within an existing trend and suggests that the trend is likely to continue. Exhaustion gap: This gap occurs near the end of a trend and signals a potential reversal.
- Plan the Entry: Once you’ve identified the gap and classified its type, determine your entry strategy. Some traders prefer to enter a trade as soon as the market opens, while others wait for a retracement or confirmation before entering.
- Set Stop-Loss and Take-Profit Levels: Determine your risk tolerance and set appropriate stop-loss and take-profit levels. Place your stop-loss order below the bullish gap or above the bearish gap to limit potential losses. Take-profit levels can be determined based on technical analysis, such as key support or resistance levels, or by using a risk-to-reward ratio.
- Risk Management: Implement proper risk management techniques, such as position sizing and risk-reward analysis, to ensure that your risk is controlled and aligned with your trading plan.
- Monitor the Trade: Once in the trade, monitor the price action and the behavior of the gap. Pay attention to any signs of reversal or continuation to adjust your trading plan if necessary.
- Exit Strategy: Determine your exit strategy based on your trading plan. This could be a predefined profit target, trailing stop-loss, or a specific technical or fundamental signal that indicates a potential reversal or loss of momentum.
Scalping is a popular intraday trading strategy that involves making multiple quick trades to take advantage of small price movements in a short period. Scalpers aim to profit from the bid-ask spread and the temporary imbalances between supply and demand. Here’s an overview of how scalping works:
- Select Liquid Instruments: Focus on highly liquid financial instruments that have tight bid-ask spreads, as this allows for quick execution and minimizes transaction costs.
- Define Timeframes: Scalping is typically conducted on short timeframes, such as one-minute, three-minute, or five-minute charts, to capture rapid price movements.

- Use Technical Indicators: Utilize technical indicators that help identify short-term momentum, volatility, and price patterns. Popular indicators for scalping include moving averages, oscillators (such as RSI or Stochastic), Bollinger Bands, or MACD.
- Set Profit Targets and Stop-Loss Levels: Determine your profit target and stop-loss levels for each trade. Scalpers often aim for small, incremental gains, such as a few ticks or pips, and implement tight stop-loss orders to limit losses if the trade goes against them.
- Execute Quick Trades: Once you identify a potential scalping opportunity based on your technical analysis, enter and exit trades swiftly to capture small price movements. Ensure that you have a fast and reliable trading platform to execute trades efficiently.
- Manage Risk and Position Sizing: Apply proper risk management techniques to ensure that no single trade poses a significant risk to your overall trading capital. Determine an appropriate position size for each trade based on your risk tolerance and account size.
- Focus on Discipline and Emotion Control: Scalping requires discipline, focus, and quick decision-making. Avoid getting emotionally attached to trades and stick to your predefined strategy.
- Monitor Market Conditions: Stay updated on market news, economic releases, and other factors that can impact short-term price movements. Scalpers need to be aware of sudden volatility or unexpected events that can influence their trades.
- Practice and Review: Scalping requires practice to develop the necessary skills and reflexes. Keep a trading journal to record your trades and review them to identify areas for improvement.
- Consider Scalping Techniques: Explore different scalping techniques, such as time and sales analysis, level 2 market depth, tape reading, or order flow analysis, to gain additional insights into market dynamics and price action.
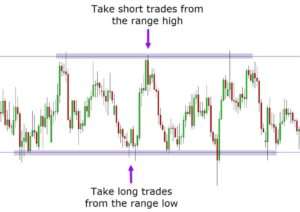
Range Trading is a strategy employed by intraday traders to take advantage of price movements within well-defined price ranges or boundaries. Traders identify support and resistance levels that contain the price action and aim to profit from buying near support and selling near resistance. Here’s an overview of how range trading works:
- Identify the Range: Look for price ranges where the asset has been trading within clear support and resistance levels. These levels can be identified using technical analysis tools such as trendlines, horizontal lines, or chart patterns like rectangles or channels.
- Confirm the Range: Verify that the price action is indeed within a range by observing multiple touches of support and resistance levels. The more times the price bounces off these levels, the stronger the range becomes.
- Plan Entry and Exit Points: Determine your entry and exit points within the range. Traders typically buy near the support level and sell near the resistance level. Some traders may also sell short near resistance and buy back near support in a bearish range.

- Set Stop-Loss and Take-Profit Levels: Establish stop-loss and take-profit levels to manage risk and secure profits. Place your stop-loss order below the support level for buy trades and above the resistance level for sell trades. Take-profit levels can be determined based on technical analysis, such as the distance between support and resistance or key price levels within the range.
- Risk Management: Implement proper risk management techniques, such as determining your position size based on your risk tolerance, to ensure that losses are controlled within your predetermined limits.
- Monitor the Trade: Once in the trade, monitor the price action within the range. Watch for signs of a potential breakout or breakdown that may invalidate the range. Adjust stop-loss and take-profit levels if necessary to protect profits or limit losses.
- Exit Strategy: Determine your exit strategy based on your trading plan. You may choose to exit the trade when the price reaches the opposite side of the range, or if you observe signs of a breakout or breakdown.
- Range Expansion: Be aware that ranges can expand or contract over time. If the range becomes narrower, it may indicate decreasing volatility, making range trading less profitable. Conversely, a breakout from the range may present new trading opportunities.
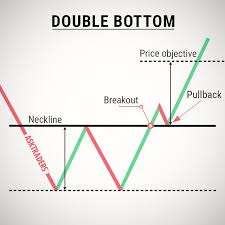
Reversal Trading is a strategy used by intraday traders to identify potential trend reversals and profit from the subsequent price movements. This strategy aims to enter trades near the end of an existing trend, anticipating a reversal and capturing profits as the new trend develops. Here’s an overview of how reversal trading works:
- Identify the Existing Trend: Determine the prevailing trend in the market, whether it’s an uptrend or a downtrend. This can be done through trendlines, moving averages, or other technical indicators.
- Look for Reversal Signals: Watch for technical indicators or chart patterns that indicate a potential trend reversal. This can include candlestick patterns, divergence in oscillators (such as RSI or MACD), or trendline breaks.

- Confirm the Reversal: Seek confirmation of the reversal signal through additional technical analysis or indicators. Multiple indicators pointing towards a reversal increase the probability of a successful trade.
- Plan Entry and Exit Points: Decide on your entry point for the reversal trade. Traders typically enter after the reversal signal is confirmed, either near support (for an upward reversal) or near resistance (for a downward reversal). Determine your exit strategy, such as a predefined profit target or a trailing stop-loss, to secure profits or limit losses.
- Risk Management: Implement proper risk management techniques, such as setting a stop-loss order, to control potential losses. Determine your position size based on your risk tolerance and the distance to your stop-loss level.
- Monitor the Trade: Once in the trade, monitor the price action and the strength of the reversal. Adjust your stop-loss and take-profit levels if necessary based on the evolving market conditions.
- Exit Strategy: Decide on your exit strategy for the trade. This could be based on technical indicators, reaching a predefined profit target, or observing signs of the reversal losing momentum.
- Consider Confirmation: Some traders prefer to wait for confirmation of the reversal by observing subsequent price action or additional signals before entering the trade. This can help filter out false reversal signals.
News Based Intraday Trading is a strategy that involves taking positions in financial instruments based on the release of significant news events or economic data. Intraday Traders aim to capitalize on the price movements triggered by the news announcements. Here’s an overview of how news-based trading works:
- Stay Informed: Keep track of economic calendars, news websites, financial news platforms, and other sources to stay updated on important news events, such as economic data releases, corporate earnings reports, central bank announcements, geopolitical developments, and industry-specific news.
- Identify Impactful News: Focus on news events that have the potential to generate significant market volatility and impact the price of the relevant financial instruments. High-impact news can lead to sharp price movements and provide trading opportunities.

- Analyze Market Expectations: Evaluate market expectations and consensus forecasts for the upcoming news event. Compare the actual released data or news with the market consensus to assess any surprises or deviations that may drive price movements.
- React Quickly: As soon as the news is released, act swiftly to take advantage of the price volatility. Monitor price action, trading volume, and the reaction of other market participants to gauge market sentiment and direction.
- Determine Trade Direction: Analyze the news release and its implications to decide whether to go long (buy) or short (sell) the financial instrument. Consider factors such as the deviation from expectations, the significance of the news event, and the potential short-term and long-term impact on the market.
- Manage Risk: Implement proper risk management techniques to protect yourself from potential losses. Set stop-loss orders to limit losses if the market moves against your position. Consider using smaller position sizes or reducing leverage for news-based trades due to the increased volatility and uncertainty.
- Monitor News Sentiment: Continuously monitor news sentiment and any subsequent developments related to the initial news event. News can have a lasting impact on market sentiment, and subsequent news releases or reactions from other market participants may affect the trade.
In conclusion, intraday trading offers the potential for quick profits and the ability to capitalize on market volatility. However, it requires disciplined decision-making, a well-defined trading plan, and effective risk management. Traders should carefully consider the costs involved and conduct thorough research and analysis before engaging in intraday trading to maximize their chances of success.


 Confirm the Trend: Verify that the price movement is indeed a sustained trend and not just a short-lived spike or temporary fluctuation. You can use technical indicators such as moving averages, trendlines, or trend-following oscillators like the MACD or the Average Directional Index (ADX) to confirm the trend.
Confirm the Trend: Verify that the price movement is indeed a sustained trend and not just a short-lived spike or temporary fluctuation. You can use technical indicators such as moving averages, trendlines, or trend-following oscillators like the MACD or the Average Directional Index (ADX) to confirm the trend.